https://roymech.co/Useful_Tables/Drive/Gears_Gearboxes.html
The late Roy Beardmore’s site is an excellent reference on gear selection options…
Types Of Gears
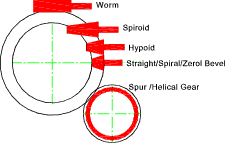
Note: More details and pictures of all gear types below are to be found at the links below table
| Type | Notes | Further Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Spur | Majority of gears are spur. Relatively easy to design and make. Parallel shafts. High efficiency (99% per train). No side thrust. Can back drive. Single Ratio up to 1:10. Can be made very accurate with low vibration /noise. Normally steel pinions require lubrication. Plastic gears can be used requiring no lubrication | Spur Gears |
| Internal Spur | Similar performance to normal spur. Results in compact drive geometry. Used in manufacture of epicyclic / planetary gears. | |
| Helical | Single Helical have similar properties to spur. However drive results in axial thrust. Gears are smoother/quieter for the same size/spec. The gears can run at high speeds up to large diameters. Higher torque/life capabilities for same size as spur. | Helical Gears |
| Double-Helical | Similar benefits to single helical but with no generated side thrust. Higher performance compared to single helical | |
| Crossed-Helical | Shaft at 90o. Difficult to make accurately. Smooth drive. | |
| Worm | Offset shafts at 90o. Very high ratios possible in single stage. Sliding action. One gear is normally copper allow (bronze). Low efficiency at higher ratios and low speeds. Lubrication essential for mechanical and thermal reasons. Cannot backdrive at high ratios. | Worm Gears |
| Bevel Gear | Mainly used for drive transmission through 90o. Only low ratios used (4:1 and less). Lubrication required. Some vibration on spur type: Helical type smoother. | Bevel Gears |
| Spiroid | Perform a similar function to worm boxes but the gears have characteristics which combine those of the bevel and worm gears. High powers and speed ratios are possible and mechanical efficiencies higher than worm boxes for equivalent ratios. | |
| Harmonic Drive | Performance advantages include high-torque capacity, concentric geometry, lightweight and compact design, zero backlash, high efficiency, high ratios (up to 320:1), and back drivability. Harmonic drive systems suffer however, from high flexibility, resonance vibration. Used in robotics | Harmonic Drives |
Brief Comparison
| Type | Normal Ratio Range | Pitch Line Velocity (m/s) | Efficiency Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spur | 1:1 to 6:1 | 25 | 98-99% |
| Helical | 1:1 to 10:1 | 50 | 98-99% |
| Double Helical | 1:1 to 15:1 | 150 | 98-99% |
| Bevel | 1:1 to 4:1 | 20 | 98-99% |
| Worm | 5:1 to 75:1 | 30 | 20-98% |
| Crossed Helical | 1:1 to 6:1 | 30 | 70-98% |
Additional Notes on Gear Efficiency
Gear Box Notes
Gearboxes Epicyclic Gears Differential Gearboxes Gear Lubrication Gear Heat Transfer